"Russia is threatening Ukraine and putting into question Europe’s security architecture. This week in Brest, EU Foreign and Defence Ministers are meeting: we should be united, clear about what we want and, above all, what we intend to do," Joseph Borrell, EU High Representative for Foreign Affairs and Security Policy says in his article, APA reports.
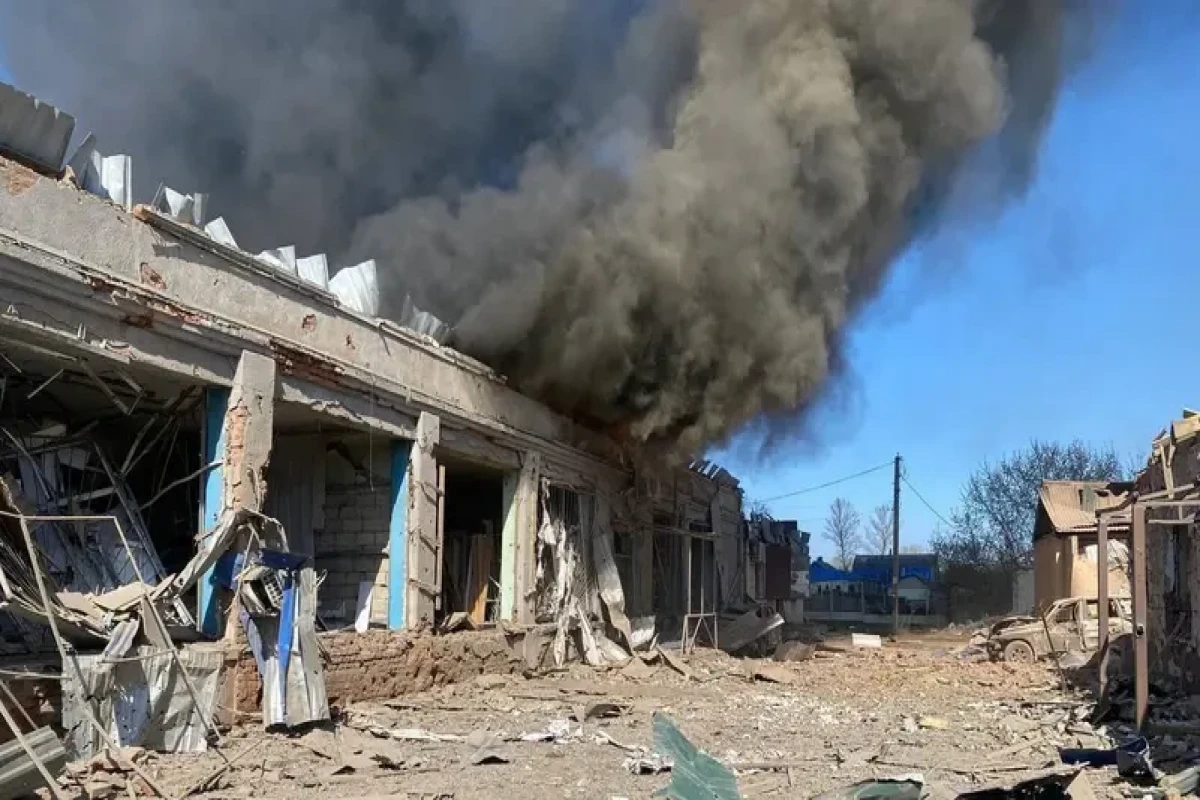
"Russia has addressed to the United States and NATO proposals on the future of security in Europe that contravene the principles of the European security architecture. They are accompanied by a military build-up on the border of Ukraine and the open threat by Russia of taking military actions if these demands are not met.
Working with the US and NATO, the EU must now define what we can do to uphold the security order of Europe and the principles underpinning it – which are clearly under threat today. This issue is on top of the agenda of the meeting of EU Foreign and Defence Ministers in Brest this week. Going into that meeting, two things are clear: we have to come to a united EU position and we have to substantiate our role, backing it up with concrete action tracks, i.e. not just on what we think or want but on what we intend to do.
The ambition of the Russian authorities is to challenge the political and security order born after the Cold War. Moscow wants to go back on the NATO-Russia founding act of 1997, which accompanied NATO’s enlargement to Central and Eastern Europe; the Paris Charter of 1990, which codified the principles for European security after the end of the Cold War.
There are three principles that Russia has previously accepted and that it now puts into question. The first is the right of each state to freely choose to belong, or not to belong, to an international organisation and to be a party to treaties or alliances, as recognised by the Paris Charter. By challenging this fundamental principle, Moscow is acting as a revisionist power. In Russia’s eyes, this prohibition would not only apply to countries of the former Soviet Union but also to EU member states like Sweden or Finland.
The second and the third are the non-use of force and the respect for the territorial integrity of all states. Russia is violating these three fundamental principles in Ukraine, as it has already done in Georgia. And Russia is not merely making assertions but accompanying this with growing military pressure on the Ukrainian border and by threatening Kyiv with a new intervention unless its demands are met in full.
In addition, Russia wants to portray the European Union as irrelevant and push for a strategic decoupling between the United States and Europe. It also seeks our acceptance of it having a decisive influence over Ukraine and Belarus, not to mention Central Asia. The fact that Central Asia is included in the stated perimeter of Russian security confirms that the question of NATO is a pretext, since no Central Asian state is a candidate for NATO membership.
In short, reconstituting the Soviet geopolitical glacis in Europe and trying for a decoupling between the United States and Europe could be the strategic objectives of Moscow.
They are clearly unacceptable. But why should we still discuss these with Moscow? First, because not discussing never helps. This week an initial set of discussions took place: on Monday between the US and Russia in Geneva, followed by NATO-Russia talks in Brussels on Wednesday. The positions remain far apart but we can envisage a continuation of a series of intense, multi-layered talks and consultations in which the EU will continue to play its full part.